Segmentation, targeting, positioning
The Critical element of Marketing
Market segmentation
You can obtain uk best quality 2025 Top best replica watches UK online. Fast shipping. Quality guarantee. Market segmentation is one of the most basic approaches of business strategy. Firms bundle customers to understand their preferences, manage relationships with best replica watches for sale them, improve product and service offerings, and assess risk.
The STP (Segmenting, Targeting, Positioning) model is useful when creating marketing communications plans since it helps marketers to prioritise propositions and then develop and deliver personalised and relevant messages to engage with different audiences. Buy AAA Best cheap cheap replica watches uk – High Quality Fake Rolex Watches For Sale.
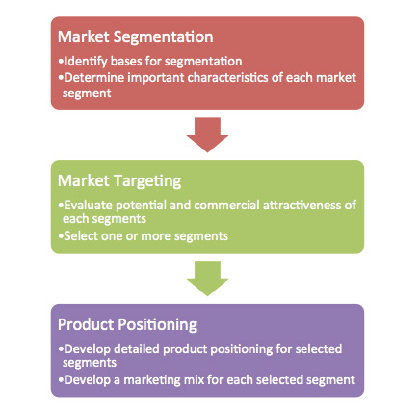
This is an audience rather than product focused approach to communications which helps deliver more relevant messages to commercially appealing audiences.
The diagram above shows how plans can have the flow from.
Well known ways to segment the audience include:
- Demographics (age, gender, income, education, ethnicity, marital status, education, household (or business), size, length of residence, type of residence or even profession/Occupation.)
- Psychographics – This refers to ‘personality and emotions’ based on behaviour, linked to purchase choices, including attitudes, lifestyle, hobbies, risk aversion, personality and leadership traits. magazines read and TV. While demographics explain ‘who’ your buyer is, psychographics inform you ‘why’ your customer buys.
- Lifestyle – This refers to Hobbies, recreational pursuits, entertainment, vacations, and other non-work time pursuits.
- Belief and Values – Refers to Religious, political, nationalistic and cultural beliefs and values.
- Life Stages – the Chronological benchmarking of people’s lives at different stages.
- Geography – Drill down by Country, region, area, metropolitan or rural location, population density or even climate
- Behaviour – Refers to the nature of the purchase, brand loyalty, usage level, benefits sought, distribution channels used, reaction to marketing factors.
- Benefit – the use and satisfaction gained by the consumer.
Targeting
The list below refers to what’s needed to evaluate the potential and commercial attractiveness of each segment.
- Criteria Size: The market must be large enough to justify segmenting. If the market is small, it may make it smaller.
- Difference: Measurable differences must exist between segments.
- Money: Anticipated profits must exceed the costs of additional marketing plans and other changes.
- Accessible: Each segment must be accessible to your team and the segment must be able to receive your marketing messages
Focus on different benefits: Different segments must need different benefits.
Product Positioning
Positioning refers to the consumer’s perception of a brand or product in relation to competing brands or products. Market positioning refers to the process of establishing the image or identity of a brand or product so that consumers perceive it in a certain way.
Positioning maps are the last element of the STP process. A positioning map is a tool that is usually used by people who are in marketing and deals with products that they are attempting to market. The idea is that everyone has a different perception of a certain product.
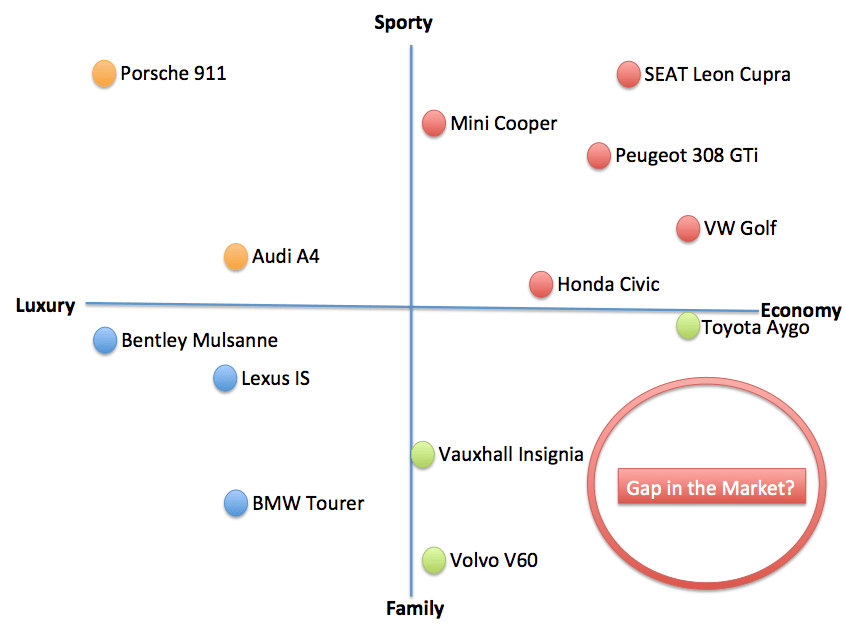
At the end of the day, it boils down to building a competitive advantage. If you think about great pianos, Steinway comes to mind. Quality cars that hold their value usually invoke thoughts of Toyota or Honda. What you’re selling doesn’t matter as much as the way it’s being sold. Of course, you can’t expect to sell a product that doesn’t work and doesn’t deliver on claims without eventually going out of business. Ultimately it’s the way you build a competitive advantage that will set your product positioning apart.
At the end of the day, it boils down to building a competitive advantage. If you think about great pianos, Steinway comes to mind. Quality cars that hold their value usually invoke thoughts of Toyota or Honda. What you’re selling doesn’t matter as much as the way it’s being sold. Of course, you can’t expect to sell a product that doesn’t work and doesn’t deliver on claims without eventually going out of business. Ultimately it’s the way you build a competitive advantage that will set your product positioning apart.

Written By
TM Nagarajan/Managing partner





